
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Management
- Advanced Endoscopy
- Upper GI Endoscopy
- Lower GI Endoscopy (Colonoscopy)
- ERCP (CBD Stone Removal / Stenting)
- EUS Guided Procedures (FNA/FNB, Drainage)
- Single / Double Balloon Enteroscopy
- Esophageal / Antral Stenting
- Esophageal & Anorectal Manometry
- Foreign Body Removal
- PEG Tube Placement
- POEM (Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy)
- STER (Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection)
- ESD (Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection)
- EMR (Endoscopic Mucosal Resection)
- Spyglass for Pancreatic Biliary Pathology
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Biliary & Pancreatic Stenting
- Anti Reflux Procedures
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Management
Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Expert Diagnosis & Endoscopic Intervention
**Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding** is a serious medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and management. It occurs when there is any bleeding from the digestive tract, ranging from subtle, chronic blood loss that leads to anemia to acute, life-threatening hemorrhage. Dr. Neeraj Dhar specializes in the rapid diagnosis and advanced endoscopic treatment of both upper and lower GI bleeding, offering life-saving interventions for patients in Faridabad.
What is Gastrointestinal Bleeding?
GI bleeding can originate from any part of the digestive tract, from the esophagus down to the rectum. It is categorized based on its location:
- Upper GI Bleeding: Occurs in the esophagus, stomach, or first part of the small intestine (duodenum). Symptoms often include vomiting blood (hematemesis, which can be bright red or "coffee ground" in appearance) and/or black, tarry stools (melena).
- Lower GI Bleeding: Occurs in the small intestine beyond the duodenum, colon, or rectum. Symptoms typically include bright red blood in the stool (hematochezia), maroon-colored stools, or black, tarry stools if the bleeding is slow and originates higher up in the small bowel.
Common Causes of GI Bleeding:
- Upper GI Bleeding Causes:
- **Peptic Ulcers:** Open sores in the lining of the stomach or duodenum.
- **Esophageal Varices:** Enlarged veins in the esophagus, often due to liver disease (cirrhosis), which can rupture and bleed profusely.
- **Gastritis/Esophagitis:** Inflammation of the stomach or esophageal lining.
- **Mallory-Weiss Tear:** A tear in the esophageal lining caused by severe vomiting or retching.
- **Esophageal/Stomach Cancer.**
- Lower GI Bleeding Causes:
- **Diverticulosis:** Small pouches (diverticula) in the colon wall that can bleed.
- **Angiodysplasia:** Abnormal, fragile blood vessels in the colon.
- **Hemorrhoids/Anal Fissures:** Common causes of minor, bright red rectal bleeding.
- **Colitis:** Inflammation of the colon (e.g., ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, infectious colitis).
- **Colon Polyps or Cancer.**
- **Ischemic Colitis:** Reduced blood flow to the colon.
Symptoms Requiring Immediate Medical Attention:
If you experience any of the following, seek immediate medical care:
- Vomiting blood (bright red or coffee-ground like)
- Black, tarry stools (melena)
- Bright red or maroon blood in stool (hematochezia)
- Severe abdominal pain
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting
- Pale skin, extreme weakness, or shortness of breath
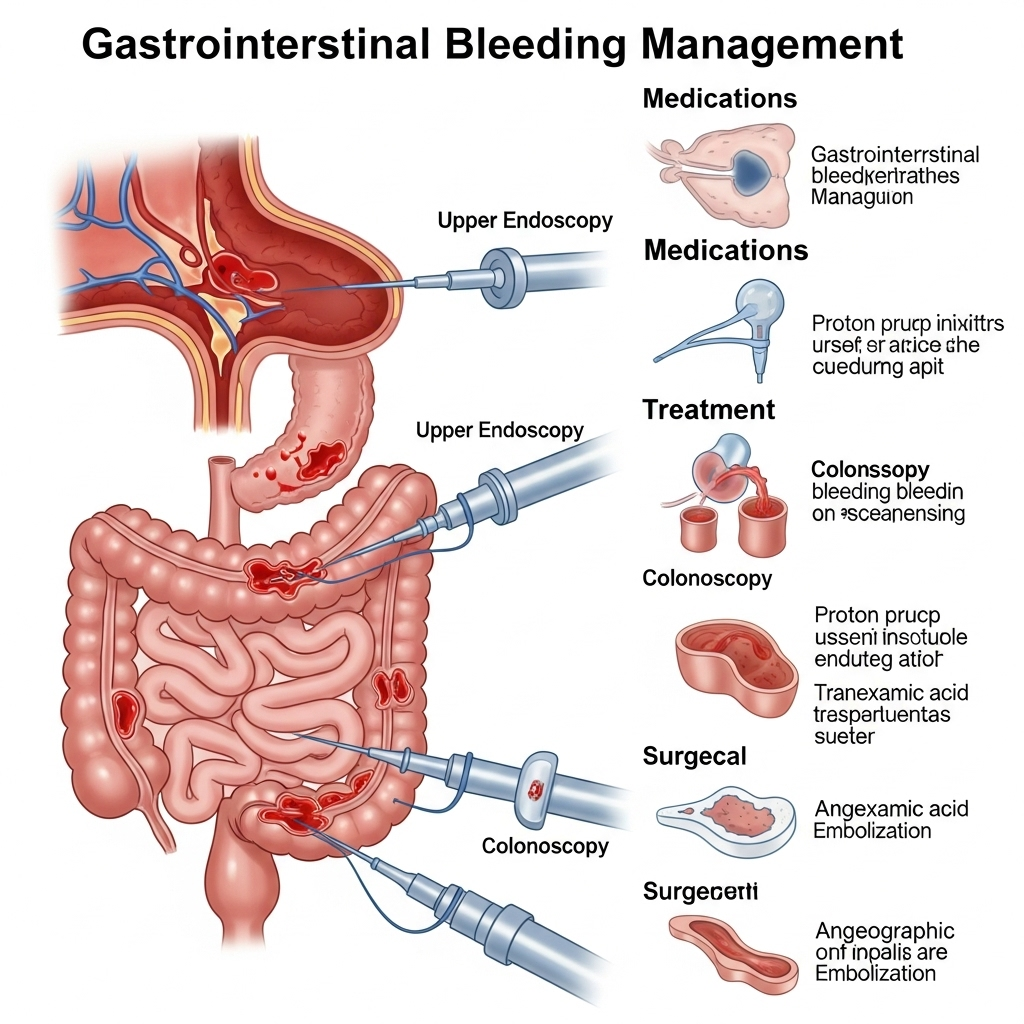
Diagnosis and Endoscopic Management:
The primary tool for diagnosing and treating GI bleeding is endoscopy:
- Initial Stabilization: Before endoscopy, the patient's condition is stabilized. This may involve intravenous fluids and, if necessary, blood transfusions.
- Upper GI Endoscopy (EGD): For suspected upper GI bleeding, Dr. Dhar performs an EGD to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. This allows for precise identification of the bleeding source (e.g., ulcer, varices, tear).
- Colonoscopy: For suspected lower GI bleeding, a colonoscopy is performed after adequate bowel preparation to examine the entire colon and rectum.
- Endoscopic Hemostasis: Once the bleeding source is identified, Dr. Dhar uses various advanced endoscopic techniques to stop the bleeding, including:
- **Injection Therapy:** Injecting epinephrine or other agents directly into the bleeding site to constrict blood vessels and promote clotting.
- **Thermal Coagulation:** Using heat (e.g., electrocautery, argon plasma coagulation - APC) to cauterize and seal bleeding vessels.
- **Endoscopic Clipping:** Applying small metal clips to close off bleeding vessels or to approximate the edges of an ulcer.
- **Band Ligation:** Specifically for esophageal varices, rubber bands are placed around the varices to cut off their blood supply and prevent or stop bleeding.
- **Suturing / Over-the-Scope Clips (OTSC):** For more complex or persistent bleeding, advanced larger clips or endoscopic suturing devices may be used.
- Post-Procedure Care: After successful hemostasis, patients are closely monitored for any signs of re-bleeding. Medications (e.g., proton pump inhibitors for ulcer bleeds) are prescribed, and a plan is made to address the underlying cause of the bleeding to prevent future episodes.
Why Choose Dr. Neeraj Dhar for GI Bleeding Management?
Dr. Neeraj Dhar is a leading gastroenterologist in Faridabad with extensive experience and expertise in the emergency diagnosis and comprehensive endoscopic management of all types of gastrointestinal bleeding. His ability to perform rapid, precise endoscopic interventions using the latest techniques is critical in controlling active bleeding and preventing re-bleeding, often averting the need for surgery. Dr. Dhar's state-of-the-art facilities and dedicated team ensure patients receive urgent, life-saving care with optimal outcomes. His focus extends beyond immediate control to identifying and managing the underlying cause, providing holistic care to his patients.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding, seek immediate medical attention. For expert diagnosis and management, contact Dr. Neeraj Dhar, a trusted name in gastroenterology in Faridabad.
