
Esophageal / Antral Stenting for Malignant Growth
- Advanced Endoscopy
- Upper GI Endoscopy
- Lower GI Endoscopy (Colonoscopy)
- ERCP (CBD Stone Removal / Stenting)
- EUS Guided Procedures (FNA/FNB, Drainage)
- Single / Double Balloon Enteroscopy
- Esophageal / Antral Stenting
- Esophageal & Anorectal Manometry
- Foreign Body Removal
- PEG Tube Placement
- POEM (Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy)
- STER (Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection)
- ESD (Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection)
- EMR (Endoscopic Mucosal Resection)
- Spyglass for Pancreatic Biliary Pathology
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Biliary & Pancreatic Stenting
- Anti Reflux Procedures
Esophageal / Antral Stenting
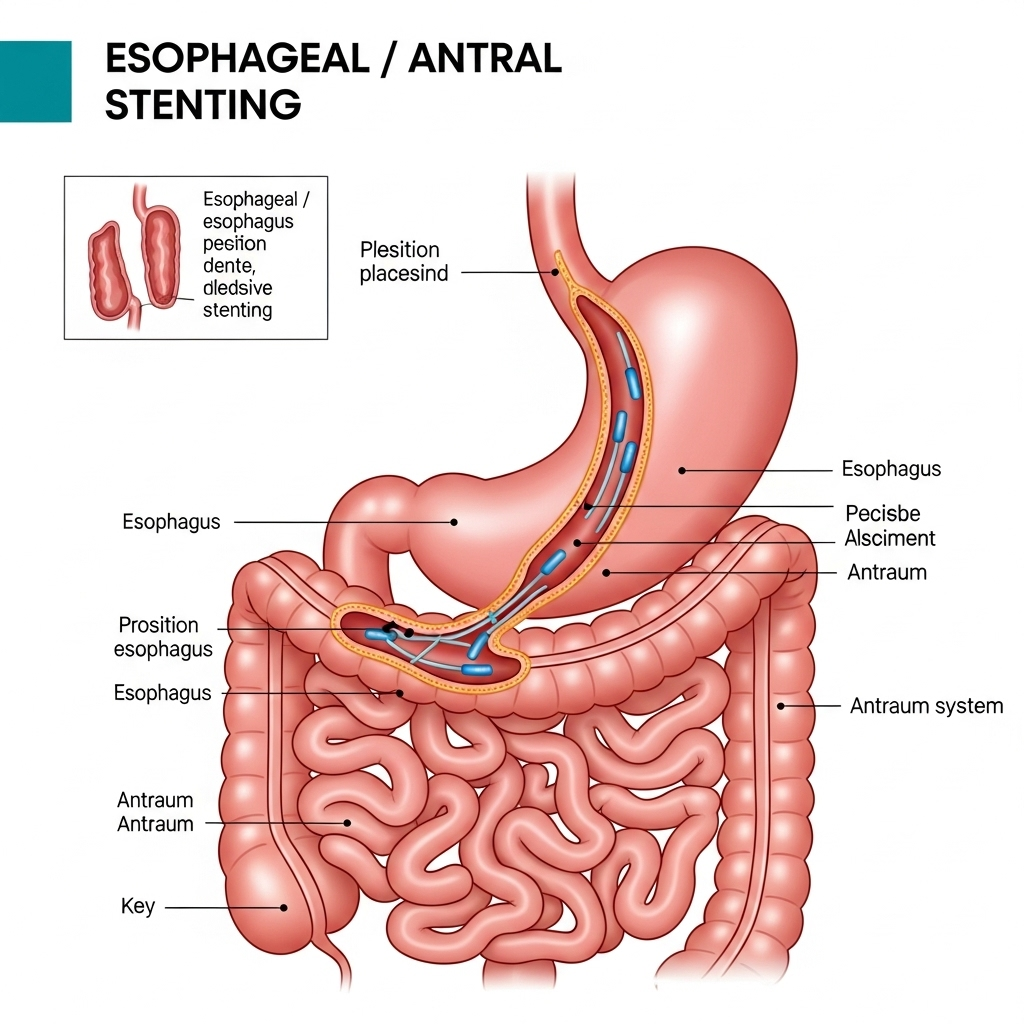
Esophageal & Antral Stenting: Restoring Passage in Malignant Obstructions
Malignant strictures (narrowing) of the esophagus or the antrum (lower part of the stomach, near the pylorus) due to advanced cancers can severely impact a patient's quality of life by causing difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or gastric outlet obstruction. **Esophageal and Antral Stenting** is an advanced endoscopic procedure designed to relieve these obstructions, allowing patients to eat, drink, and maintain nutrition, significantly improving their comfort and overall well-being.
What is GI Stenting for Malignant Growth?
During this procedure, Dr. Neeraj Dhar uses an endoscope to guide the placement of a **Self-Expandable Metallic Stent (SEMS)** across the narrowed area caused by the tumor. These stents are made of a flexible mesh material that is compressed into a thin tube for delivery. Once deployed, the stent gradually expands, creating an open通道 through the obstruction. This allows food and liquids to pass more easily (in the esophagus) or enables gastric contents to empty properly into the small intestine (in the antrum/pylorus).
Why is Esophageal / Antral Stenting Performed? (Indications)
Stenting is primarily a palliative measure used to improve symptoms and quality of life for patients with malignant obstructions when surgical resection is not an option or is postponed. Key indications include:
- Esophageal Cancer: To relieve severe dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) and allow patients to eat and drink normally, reducing the need for alternative feeding methods.
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction: Caused by tumors in the antrum or pylorus (the exit of the stomach), leading to persistent vomiting, nausea, and inability to eat. Stenting helps restore gastric emptying.
- Improving Nutrition: By enabling food intake, stenting helps maintain nutritional status, which can be crucial for patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Rapid Symptom Relief: Stenting offers quick improvement of obstructive symptoms, often within a day or two, enhancing patient comfort.
Types of Stents Used:
The most common type of stent used is the **Self-Expandable Metallic Stent (SEMS)**. These can be:
- Uncovered Stents: Bare metal stents, suitable for certain types of strictures.
- Covered Stents: Have a synthetic membrane covering to prevent tumor ingrowth and facilitate removal if needed. These are often preferred for malignant obstructions.
Preparation for the Procedure:
Proper preparation ensures the safety and success of the stenting procedure:
- Fasting: You will need to fast for at least 6-8 hours before the procedure (no food or drink) to ensure the upper GI tract is empty.
- Medication Review: Inform Dr. Dhar about all your medications, especially blood thinners, as adjustments or temporary discontinuation may be necessary to minimize bleeding risk.
- Imaging Review: Recent imaging (CT scan, previous endoscopy reports) will be reviewed to precisely plan the stent placement.
- Arranging for a Ride: Since you will receive sedation, you must arrange for someone to drive you home after the procedure and stay with you for a few hours.
What to Expect During the Procedure:
- You will receive **conscious sedation** intravenously to help you relax and minimize discomfort. General anesthesia may be used in certain complex cases.
- You will lie comfortably, and an endoscope will be gently passed through your mouth to visualize the stricture.
- Under direct endoscopic and fluoroscopic (X-ray) guidance, a guidewire will be carefully advanced through the narrowed segment. The stent, compressed into a narrow catheter, is then threaded over this guidewire and precisely positioned across the obstruction.
- Once in position, the stent is deployed and allowed to expand. Dr. Dhar will confirm its proper placement and expansion using both endoscopy and fluoroscopy.
- The procedure typically takes 30-60 minutes.
Recovery and Post-Procedure Care:
- After stenting, you will be monitored in a recovery area until the effects of sedation wear off.
- You may experience some mild discomfort or chest pain (for esophageal stents) for a day or two as the stent fully expands. Pain relief can be provided.
- You will be instructed to start with a liquid diet, gradually advancing to a soft, pureed diet as tolerated, typically within 24-48 hours. Chewing food thoroughly is important.
- It's crucial to avoid driving, operating machinery, or making important decisions for the rest of the day due to the lingering effects of sedation.
- You will receive specific dietary advice to prevent food impaction and ensure stent patency.
Why Choose Dr. Neeraj Dhar for Esophageal / Antral Stenting?
Dr. Neeraj Dhar is a highly experienced and skilled gastroenterologist in Faridabad with extensive expertise in complex therapeutic endoscopic procedures, including the precise and safe placement of esophageal and antral stents for malignant obstructions. His proficiency ensures optimal stent deployment, leading to significant symptom relief and improved quality of life for patients battling advanced GI cancers. Dr. Dhar uses state-of-the-art endoscopic equipment and follows best practices, providing compassionate and effective palliative care to his patients.
If you or a loved one is facing challenges due to a malignant obstruction in the esophagus or stomach, consult Dr. Neeraj Dhar for expert evaluation and consideration of stenting as a highly effective palliative solution.
